How to Fix the P0420 Trouble Code
2023-06-13 by UDIAG
OBD-II Trouble Codes serve as essential diagnostic tools in modern vehicles, providing insights into various engine and emission-related issues. Among these codes, the P0420 Trouble Code stands out as a common and significant problem. In this essay, we will delve into the details of the P0420 code, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and potential fixes.
Understanding P0420 OBD-II Trouble Code
The P0420 OBD-II Trouble Code is a diagnostic trouble code that is specific to vehicles equipped with onboard diagnostics systems. It indicates a problem with the efficiency of the catalytic converter in the vehicle’s exhaust system.
The catalytic converter plays a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions by converting toxic gases, such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons, into less harmful substances. It contains catalysts that facilitate chemical reactions to convert these pollutants into carbon dioxide, water vapor, and nitrogen.
The P0420 code is triggered when the vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU) detects that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently. This means that the converter is not effectively reducing emissions to the levels required by the vehicle’s emission standards.
Causes of P0420 Code
The P0420 code can be triggered by several factors related to the efficiency of the catalytic converter. Here are some common causes:
- Faulty Catalytic Converter: Over time, the catalytic converter can deteriorate or become damaged. Age, physical impact, or contamination from oil or coolant leaks can contribute to its inefficiency. A degraded or failed catalytic converter will often trigger the P0420 code.
- Malfunctioning Oxygen Sensors: Oxygen sensors (O2 sensors) are responsible for measuring the oxygen content in the exhaust gases before and after they pass through the catalytic converter. If the oxygen sensors become slow or unresponsive, they can provide inaccurate readings to the vehicle’s ECU, leading to the activation of the P0420 code.
- Engine Misfires: Engine misfires can introduce unburned fuel into the exhaust system, affecting the catalytic converter’s efficiency. Misfires may occur due to issues such as faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, or engine timing problems. The presence of engine misfires can trigger the P0420 code.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system before the catalytic converter can introduce excess oxygen into the exhaust stream. This can cause false readings from the oxygen sensors, resulting in the activation of the P0420 code. Common sources of leaks include damaged or deteriorated exhaust manifold gaskets, cracked exhaust pipes, or loose connections.
- Fuel System Problems: Issues with the fuel system, such as a malfunctioning fuel injector or a clogged fuel filter, can disrupt the proper air-fuel mixture required for efficient combustion. This can lead to increased emissions and reduced catalytic converter efficiency, triggering the P0420 code.
Symptoms of P0420 Code
When the P0420 code is triggered, several symptoms may manifest in the vehicle. Here are common symptoms associated with the P0420 code:
- Illuminated Check Engine Light: The most noticeable symptom is the illumination of the check engine light (CEL) on the vehicle’s dashboard. The CEL serves as a warning that a problem has been detected in the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system, including issues related to the catalytic converter.
- Decreased Fuel Efficiency: A decrease in fuel efficiency is often observed when the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently. The converter’s reduced ability to convert harmful gases can result in an incomplete combustion process, leading to increased fuel consumption and decreased mileage per gallon.
- Reduced Engine Performance: The engine’s performance may be adversely affected when the catalytic converter is not operating optimally. The converter plays a role in maintaining proper exhaust flow, and any restriction or inefficiency can impact engine power, responsiveness, and overall performance.
- Unusual Exhaust Odors: When the catalytic converter is not functioning as it should, there may be a noticeable change in the smell of the exhaust gases. A faulty converter can emit strange or pungent odors, such as a rotten egg smell, indicating incomplete conversion of the exhaust gases.
Diagnosing P0420 Code with UDIAG X-30
Diagnosing the P0420 code using UDIAG car diagnostic tools can be an effective and convenient way to identify the underlying issue with the catalytic converter. Here are the steps to diagnose the P0420 code using UDIAG X-30:
#1 Connect the UDIAG X-30: Plug the UDIAG X-30 into the OBD-II port with VCI, which is usually located under the dashboard or steering column of the vehicle. Ensure that the ignition is turned off before connecting the tool.
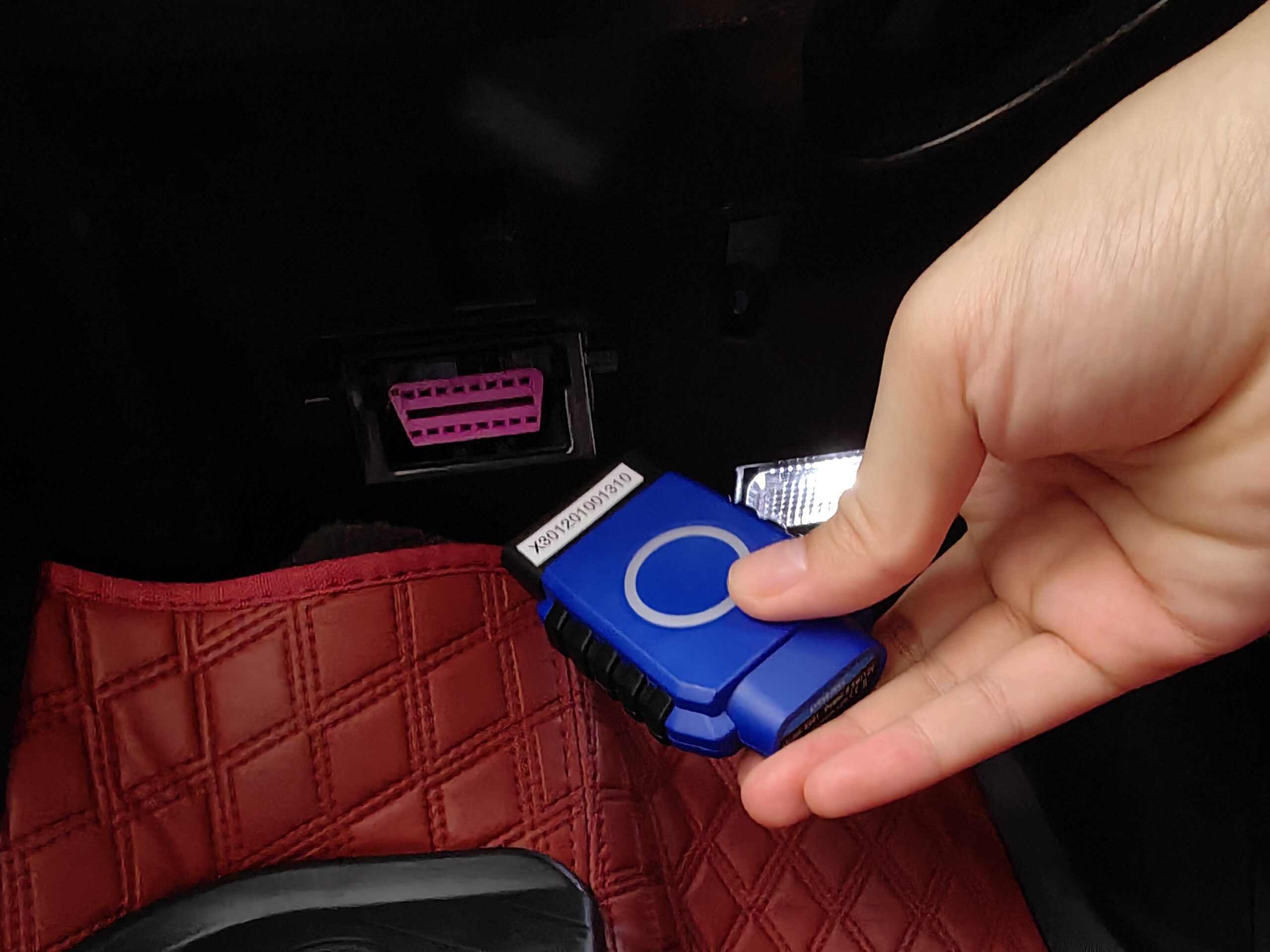

#2 Power on the diagnostic tool: Turn on the UDIAG X-30 and wait for it to establish a connection with the vehicle’s onboard computer system. This may take a few seconds.
#3 Retrieve error codes: Access the “Diagnostic” section of the UDIAG tool’s menu. It will display a list of error codes stored in the vehicle’s ECU. Look for the P0420 code specifically related to the catalytic converter.
#4 Interpret the code: Once the P0420 code is identified, review its description and associated information provided by the UDIAG tool. This will give you insights into the possible cause of the code, which is related to the catalytic converter’s efficiency.
#5 Perform additional system checks: UDIAG tools provide additional diagnostic functions, such as live data monitoring or component testing. Utilize these features to further evaluate the oxygen sensors, engine misfires, exhaust leaks, or fuel system issues that can contribute to the P0420 code.
#6 Inspect the catalytic converter: Conduct a visual inspection of the catalytic converter, checking for physical damage, leaks, or signs of contamination. Ensure there are no loose connections or detached components in the exhaust system.
#7 Test the oxygen sensors: Use the UDIAG X-30 to monitor the oxygen sensor readings in real-time. Compare the readings from the pre-catalytic converter and post-catalytic converter sensors to verify their functionality. If the readings are inconsistent or the sensors are unresponsive, they may need to be replaced.
#8 Evaluate overall performance: Assess the vehicle’s overall performance, including engine power, fuel efficiency, and exhaust emissions. While not exclusive to the P0420 code, any noticeable issues can provide further insights into the catalytic converter’s efficiency.
By utilizing UDIAG car diagnostic tools, you can effectively retrieve and interpret the P0420 code, perform system checks, and evaluate the catalytic converter’s performance. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for using the UDIAG tool and consult a qualified mechanic or repair professional if further inspection or repairs are needed based on the diagnostic results.
Fixing P0420 Code
Fixing the P0420 trouble code depends on the underlying cause of the issue. Here are some common steps that can be taken to address the P0420 trouble code:
- Verify the code: Before proceeding with any repairs, it’s important to ensure that the P0420 code is accurately diagnosed. Double-check the code using a diagnostic tool to confirm that it is indeed related to the catalytic converter.
- Inspect the catalytic converter: Conduct a visual inspection of the catalytic converter. Look for signs of physical damage, leaks, or contamination. Ensure that it is securely attached to the exhaust system and that there are no loose connections.
- Repair exhaust leaks: If any exhaust leaks are detected before the catalytic converter, repair them promptly. Leaks can introduce excess oxygen into the exhaust stream, leading to false readings and triggering the P0420 code.
- Replace faulty oxygen sensors: If the oxygen sensors are found to be faulty or providing inaccurate readings, they should be replaced. Both the pre-catalytic converter and post-catalytic converter sensors should be inspected and replaced if necessary. Ensure that the new sensors are compatible with the vehicle’s make and model.
- Address engine misfires: Engine misfires can affect the efficiency of the catalytic converter. If misfires are identified, diagnose and repair the underlying issues causing them. This may involve replacing faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or addressing other ignition system problems.
- Clean or replace the catalytic converter: In some cases, the catalytic converter may become clogged or contaminated, leading to reduced efficiency. Depending on the severity of the issue, it may be possible to clean the converter using specialized cleaning solutions. If cleaning is not effective, replacing the catalytic converter with a new one may be necessary.
- Reset the check engine light: After addressing the underlying issues, use a diagnostic tool to clear the P0420 trouble code and reset the check engine light. This will allow you to monitor the system and ensure that the repairs have been successful.
Preventive Measures
Taking preventive measures can help reduce the likelihood of encountering the P0420 trouble code and ensure the long-term health of the catalytic converter. Here are some preventive measures to consider:
- Follow recommended maintenance schedules: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance intervals for your vehicle, including regular tune-ups, oil changes, and scheduled inspections. This helps keep the engine running smoothly and reduces the risk of issues that can impact the catalytic converter’s efficiency.
- Use high-quality fuel and additives: Opt for high-quality gasoline that meets the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications. Avoid using low-quality or contaminated fuel, as it can lead to engine misfires and affect the catalytic converter’s performance. Additionally, consider using fuel additives designed to clean the fuel system and help maintain proper combustion.
- Address engine issues promptly: Address any engine problems promptly to prevent them from affecting the catalytic converter. Misfires, faulty spark plugs, ignition system issues, or fuel system problems can contribute to the P0420 code. Regularly monitor the vehicle’s performance and address any issues as soon as they arise.
- Avoid aggressive driving and excessive idling: Aggressive driving habits, such as rapid acceleration and sudden braking, can put additional stress on the engine and exhaust system. Additionally, excessive idling can cause the catalytic converter to overheat. Drive responsibly and avoid prolonged idling whenever possible.
- Inspect the exhaust system regularly: Perform visual inspections of the exhaust system, including the catalytic converter, for signs of damage, leaks, or loose connections. Address any issues promptly to prevent them from worsening and affecting the converter’s efficiency.
- Use compatible aftermarket parts: If replacement parts are needed for the vehicle’s exhaust system, such as oxygen sensors or the catalytic converter itself, ensure they are compatible with the vehicle’s make and model. Using non-compatible or low-quality aftermarket parts can affect the performance and longevity of the converter.
- Avoid overloading the vehicle: Excessive weight or overloading the vehicle can put additional strain on the engine and exhaust system. This can affect fuel efficiency and increase the risk of damage to the catalytic converter. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended weight limits and avoid carrying unnecessary loads.
Conclusion
The P0420 OBD-II Trouble Code is an important indicator of potential problems with the catalytic converter. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and diagnostic procedures is crucial for effective repairs. By promptly addressing issues related to the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, engine misfires, and exhaust leaks, vehicle owners can ensure optimal performance and reduce harmful emissions. Regular maintenance and preventive measures contribute to the long-term health and efficiency of the vehicle, benefiting both the owner and the environment.


